Our series: Supply Chain Simulation / Part 6
Solutions to location problems with greenfield analysis
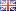
Greenfield analysis (GFA), sometimes called centroid analysis, is a supply chain network design method often used in the early stages of supply chain planning. RIA helps effectively solve a location problem, such as determining the best locations as well as the optimal number of distribution centers (DCs) or production facilities.
RIA should be the first step in supply chain network planning. You do not need to come up with options for locations of DCs or manufacturing facilities to conduct RIA; the role of RIA is to provide you with just those options.
Greenfield analysis assumes a high level of abstraction, so only a minimal amount of detail is required:
- Customer locations
- Products
- Demand for each customer and product
The result of the analysis is an optimal location for a production or warehouse facility where the cost of all inbound and outbound transportation is minimized. This optimal point is called the center of gravity.
Basic RIA does not take into account roads, cities, geographic features, etc. – it simply provides an optimal mathematical solution. More advanced variants include RIA with roads and brownfield analysis.
The results of an RIA can be used in a subsequent supply chain network optimization to determine the optimal locations from several proposed and more realistic options.